The Science
The Secret Sauce
REMEDiAg’s products are liquid fertilisers with lipid-encapsulation capabilities. The encapsulation of nutrient compounds optimises the nutrient use efficiency in the plant system to deliver a broad spectrum of benefits to plant growth, enhance stress resistance and immune responses, increase crop yield and promote more robust and healthier crops.
A breakthrough
in plant health
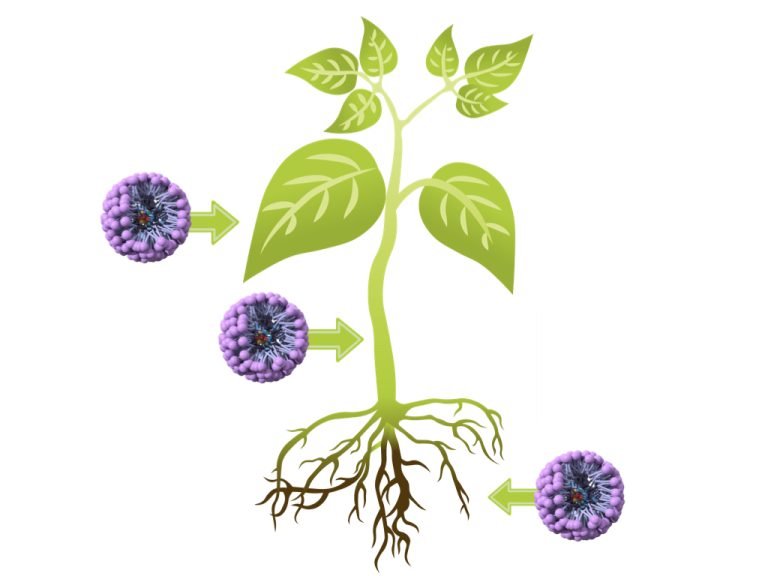
The lipid-encapsulation capability allows it to move quickly through the symplastic pathways in plants, delivering high efficacy and effectively providing a systemic mode of action. The encapsulated micelles can penetrate the stems or trunk, move into the vascular system of woody crops to mitigate vascular diseases and provide benefits or protection throughout the plant’s system.
REMEDiAg products are recognised in Europe, Latin America and Asia as valuable tools for precision crop management. Their encapsulation characteristics enhance the efficacy of active compounds and chemicals.
Our products raise the efficacies of substances and optimise the input of chemicals onto crops, thereby improving food safety, agriculture and environmental sustainability.
About Our Lipid Technology
Contains a lipid emulsion known as organic colloidal concentrate or OCC
Encapsulates active compounds to improve uptake and efficacies
Protects and stabilises active compounds, including biologicals
Provides a systemic mode of action in plants and raises the availability of soil nutrients
Compatible with many commercially available active compounds
Eligible for organic input accreditation
Characteristics of REMEDiAg Products
Elicits prolonged nanobubbles with hydrogen peroxide as an alternative measure for zero-residue crop protection against fungal, viral and anaerobic bacterial conditions.
It is cost-effective in enhancing the efficacy of chemical compounds.
Encapsulates compounds and moves them via the symplastic pathways through the membrane cell walls of plant cells resulting in superior uptake and penetration of nutrients.
Effective in the supply of compounds in the xylem and phloem through the foliage, trunk, bark or the root system.
Why use REMEDiAg Products?
Improve profits for
all stakeholders
Help mitigate production losses from challenging diseases
Optimise inputs to facilitate sustainable agriculture
Improve the quality of
attributes of the output
How do REMEDiAg Products work?
The lipids disperse within the aqueous environment.
The lipids encapsulate minerals and compounds to form micelles.
The charged micelles activate receptors on the cell walls in the plant system.
Plant cells absorb the micelles with encapsulated substances.
Lipid Encapsulation – A Vital Delivery Function
Lipid encapsulation is the process of enclosing or encapsulating active substances or compounds within lipid-based carriers or vesicles. These lipid-based carriers, called micelles, liposomes or lipid nanoparticles, can protect the encapsulated substances and enhance their delivery and efficacy. While lipid encapsulation does not directly contribute to plant growth, it can positively affect plant health and development through improved nutrient uptake, enhanced protection against stressors, and targeted delivery of bioactive compounds. Here are some ways in which lipid encapsulation can contribute to plant growth:
1. Nutrient Delivery
Lipid encapsulation can improve the delivery and availability of essential nutrients to plants. Encapsulating nutrients, such as micronutrients or beneficial compounds, within lipid carriers can enhance their stability, solubility, and targeted delivery to plant roots. This can help overcome nutrient deficiencies and promote optimal plant growth and development.
2. Controlled Release of Bioactive Compounds
Lipid encapsulation allows for the controlled release of bioactive compounds, such as plant growth regulators or beneficial microorganisms. The lipid carriers can protect these compounds from degradation or loss, ensuring their sustained release and activity in the plant's rhizosphere or internal tissues. Controlled release systems can enhance the efficacy of bioactive compounds, resulting in improved plant growth, stress tolerance, and disease resistance.
3. Protection Against Environmental Stressors
Lipid encapsulation can protect against environmental stressors, such as drought, temperature extremes, or pathogen attacks. Encapsulated compounds can act as stress protectants by improving the plant's tolerance and recovery from adverse conditions. This can enhance plant growth, reduce damage, and improve plant health.
4. Enhanced Uptake of Pesticides or Agrochemicals
Lipid encapsulation of pesticides or agrochemicals can improve their efficacy and reduce potential negative impacts on the environment. The encapsulated formulations can improve the targeted delivery of these compounds to specific plant tissues or pests, reducing off-target effects and minimising their widespread use. This can contribute to sustainable agriculture practices and promote healthier plant growth.
Questions & Answers
Why do I need REMEDiAg Lipid Technology?
It enhances the efficacies of active compounds by 2x or more and prolongs their effects on crop growth. Hence, whether a formulator, private label distributor or grower, you can optimise input costs while improving the performance of your products, resulting in higher profits while facilitating environmental sustainability.
Have REMEDiAg products been proven in the field?
They have undergone more than ten years of field studies and research with major global food brands and companies across Asia, Europe, Africa, Australasia, and North and South America. They have been proven effective on various crops, from cereals to fruit trees, vines, horticulture, root crops, and nurseries of the forestry industry.
How can I be sure that the products can work in my fields or on my crops?
REMEDiAg products are science-based. While agriculture is affected by environmental factors that impact crop growth, the science behind crop health and development remains the same. Hence, although there are variances in ecological factors, they work the same despite the environmental differences.
What compounds are REMEDiAg products compatible with?
REMEDiAg products have been applied in the field for over ten years with a wide range of active compounds in fertilisers, insecticides, fungicides, bactericides, and herbicides. It improved their efficacies by 2x, and in some instances, more than 2x. For more information, please get in touch with us for a list of active compounds applied with REMEDiAg products in the field over the years with proven efficacies.
What can REMEDiAg products do for biologicals?
The lipids in them work as excellent stabilisers and carriers for biologicals and can help protect these sensitive compounds from degradation, temperature changes, and other environmental factors. They can also help extend the shelf-life of biological products by shielding them with encapsulated lipids. The results will depend on the nature and characteristics of the biologicals.
Growers’ experiences in using our products
Facilitates early maturity and harvest of seasonal high-value crops by more than two weeks to capitalise on higher returns in the market
Mitigates production losses from challenging diseases such as -
In Brazil - Citrus Greening (HLB)
In Mexico - Fusarium root rot in berries
In Portugal - xyella fastidiosa on almond and olive trees and grapevine trunk disease in vineyards
In Spain - Grapevine trunk disease in vineyardsReduces input costs by 50% while improving production yields by more than 20 %
In China - on plantations
In Europe - in horticulture, fruit orchards and broadacre cereal crops
In South America - in horticulture, fruit orchards, sugar cane and broadacre cereal cropsShortens nursery to field lead time by 30% with improved field survival rates by more than 20%.
Enables low residue cultivation while protecting the crops for optimal yields.
Examples from the field
Passion Fruit
Cherry Tomatoes
Orchids
Roses
Pasture
Soy Bean
Maize
Raspberries
Agave
Japanese Plum
Garlic
Surfinia Burgundy
Sweetsop
Iceberg Lettuce
Bitter Melon
Durians
Beans
Pineapples
Other Asian Results
Chestnut Tree
Maple Tree